What Is the Largest Instrument Family?
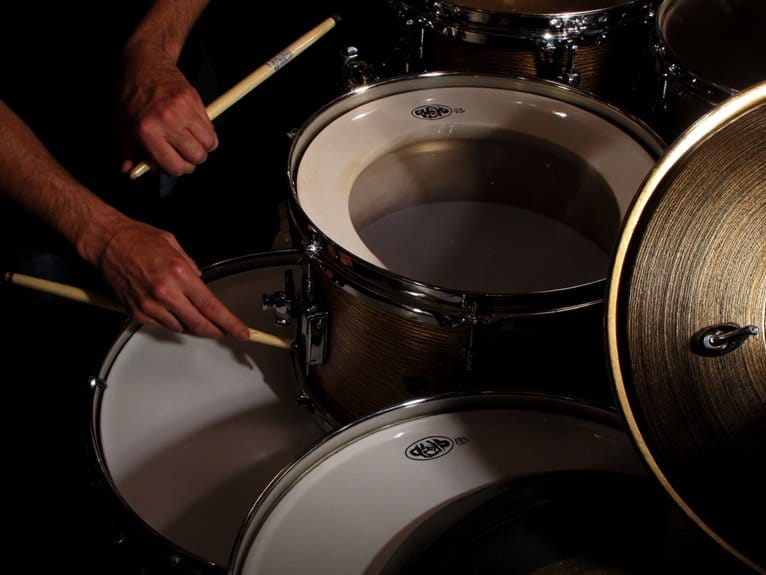
The percussion family is the largest and most diverse group of instruments in the orchestra, encompassing a vast array of categories and subcategories that produce a wide range of sounds and textures. From traditional instruments like drums and timpani to unconventional objects repurposed as percussion members, this family's unique sonic capabilities and dynamic expressive range have evolved substantially over time. With its cultural importance, role in classical music, and importance in rhythm sections, the percussion family plays a vital role in shaping the sonic landscape of orchestral music. As we delve its complexities, the richness of this family is further revealed.
We are supported by our audience. When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission, at no extra cost for you. Learn more.
Defining the Percussion Family
The percussion family, comprising the largest and most diverse group of instruments in the orchestra, is characterized by its unique sonic capabilities and dynamic expressive plummet. With a rich percussion history spanning thousands of years, instruments have evolved substantially over time. From ancient civilizations to modern ensembles, the percussion family has undergone substantial transformations. Instrument evolution has led to the development of new sounds, techniques, and playing styles. This diversity is reflected in the wide range of instruments, from drums and cymbals to xylophones and gongs. As the largest instrument family, percussion instruments play a crucial role in shaping the sonic landscape of orchestral music.
Types of Percussion Instruments
Percussion instruments encompass a vast array of categories, each distinguished by its unique sound production mechanism and acoustic properties. Within this diverse family, we find membranophones, such as drums and timpani, which produce sound through vibrating membranes. Idiophones, like cymbals and gongs, generate sound through the vibration of the instrument itself. Chordophones, including instruments like the guitar and harp, produce sound through vibrating strings. The innovation of new instrument designs has led to the development of novel percussion instruments, expanding the possibilities for musical expression. Furthermore, percussion therapy has emerged as a valuable tool for promoting physical and emotional well-being. By delving into the various types of percussion instruments, we can appreciate the rich complexity and versatility of this instrument family.
Unconventional Percussion Members
Beyond traditional instruments, a diverse range of unconventional objects has been repurposed as percussion members, challenging conventional notions of sound production and expanding the creative possibilities of the percussion family by taking a leap. Found sound experimentation has led to the incorporation of everyday objects, such as metal pipes, glass bottles, and wooden blocks, into percussion ensembles. These unconventional members not only produce unique timbres but also facilitate instrumental storytelling, where the sounds evoke narratives and emotions. By exploring the sonic potential of these objects, percussionists can craft distinctive soundscapes that engage and enthrall audiences. This innovative approach has substantially broadened the scope of the percussion family, enabling musicians to push the boundaries of musical expression.
Cultural Significance of Drums
Drums, as a fundamental component of the percussion family, have played a pivotal role in shaping cultural identities across various societies, with their rhythmic pulses often serving as a heartbeat that resonates deeply with communal values and traditions. In Ancient Civilizations, drums were used in Drumming Rituals to communicate with deities, ancestors, and spirits, and to accompany ceremonies, dances, and storytelling. The rhythmic patterns and beats conveyed emotions, told stories, and preserved cultural heritage. Drums also played a vital role in communal gatherings, festivals, and celebrations, fostering social cohesion and unity. Through their dynamic sounds and expressive movements, drums have been instrumental in perpetuating cultural traditions and values, leaving an indelible mark on the fabric of human societies.
Percussion in Classical Music
Throughout the evolution of classical music, a diverse array of percussion instruments has been integrated into orchestral ensembles, gradually expanding the timbral palette and dynamic range of composers' creative expressions as they descend. Percussion evolution in classical music has been shaped by the incorporation of various instruments, such as timpani, snare drums, and cymbals, which have added complexity and nuance to compositions. Classical improvisation has also played a significant role, allowing percussionists to experiment with unconventional techniques and sounds. This fusion of traditional and innovative approaches has enriched the classical music repertoire, offering a kaleidoscope of textures and moods. As a result, percussion has become an indispensable component of classical music, elevating the art form to new heights.
The Role of Rhythm Sections
In classical music, the rhythm section, comprising instruments such as basses, cellos, and harps, provides harmonic foundation and rhythmic pulse, underscoring its essential role in shaping the overall musical structure. This section's primary function is to establish a sense of rhythm dynamics, which in turn influences the instrumental texture of the entire ensemble. By doing so, the rhythm section creates a sonic framework that supports the melodic lines and harmonies, thereby adding depth and complexity to the music. The careful balance of rhythm and harmony enables the rhythm section to subtly modulate the overall musical atmosphere, making it a crucial component of classical music composition.
Exploring Percussion Subcategories
Six primary subcategories of percussion instruments exist, each distinguished by its unique sonic characteristics and roles within the ensemble. These subcategories include membranophones, idiophones, chordophones, aerophones, electrophones, and instrumental hybrids. Membranophones, such as drums, produce sound through vibrating membranes, while idiophones, like cymbals, generate sound through the vibration of the instrument itself. The evolution of percussion has led to the development of instrumental hybrids, which combine elements of multiple subcategories. For instance, the drum-machine hybrid has transformed modern music production. Understanding these subcategories is essential for appreciating the complexity and diversity of percussion instruments, as well as their role in shaping musical compositions. By exploring these subcategories, musicians and composers can release new sonic possibilities and push the boundaries of percussion evolution.